-
Anesthesia Mask Seal Technology: Preventing Gas Leaks And Occupational Exposure
Views: 222 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-06-25 Origin: Site
In the operating room (OR), the anesthesia mask is more than a simple conduit for delivering gases—it is the frontline barrier between sterile airway management and the surrounding environment. A reliable mask seal prevents anesthetic gas leaks that can expose staff to harmful waste gases, while simultaneously blocking pathogens from entering the patient's airway or escaping into the room. With healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and occupational exposure both under intense scrutiny, modern seal technology must deliver a dual function: flawless containment of both microbes and gas. In this article, we explore how advanced seal designs in anesthesia masks strengthen infection control, protect healthcare workers, and maintain patient safety.
Mask Handling and Touchpoints: Seals vs. Headgear Adjustments
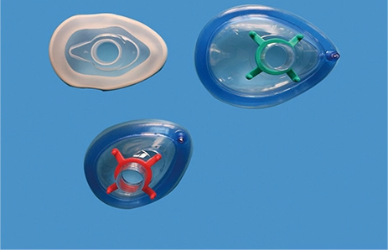
Every surface touched in the OR has the potential to transfer microorganisms or anesthetic gas residues. Traditional anesthesia masks consist of two primary components: the soft seal (or cushion) that contacts the patient's face, and the headgear that secures the mask in place.
Seal Contact Points
The seal is custom-shaped to conform to facial contours—around the nose bridge, cheeks, and chin. Proper fit demands staff to adjust the mask cushion until no gaps remain. Each adjustment introduces a risk of contamination: fingertips transferring skin flora or environmental microbes to the seal surface, which may then contact the patient's skin or mucosa.Headgear Manipulation
Headgear straps often require multiple tensioning steps: tightening above the head, below the ears, and sometimes at mid-strap points. Clinicians frequently fine-tune strap tension during the procedure, adding more touchpoints and further opportunities for contamination. Additionally, poorly designed buckles or clips can trap fluids and secretions, making effective cleaning or disinfection challenging.
By contrast, masks with integrated, single-use seal assemblies drastically reduce handling steps. Seals pre-bonded to masks eliminate repetitive contact with separate cushions, while streamlined headgear systems—such as one-piece disposable straps—cut down on adjustments. Fewer touchpoints mean fewer opportunities for microbial transfer, supporting stricter aseptic technique.

Microbial Ingress Pathways in Poorly Sealed Systems
A suboptimal mask seal is not only inefficient for gas delivery; it also creates pathways for microbial ingress and egress:
Patient-to-Mask Transfer
Exhaled droplets and aerosolized particles can deposit on the inner mask surface. If the seal is loose, these contaminated droplets can pool in mask crevices or migrate to headgear components, which may later be handled by staff.Mask Surface Biofilm
Reusable cushions develop biofilms over time when cleaning protocols are imperfect. Biofilms protect bacteria from disinfectants, turning mask surfaces into persistent reservoirs for pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus or Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Environmental Contamination
Gaps in the seal allow anesthetic gases—and any suspended pathogens in exhaled breath—to leak into the ambient OR air. In high-traffic areas, these aerosols can settle on nearby equipment, drapes, or personnel, increasing HAI risk and occupational exposure.Cross-Patient Transmission
Reusable masks and cushions that are inadequately sterilized can harbor patient-derived organisms. When deployed on the next patient, these microbes may colonize skin or mucosal surfaces, leading to surgical site infections or pneumonia.
Effective seal technology closes these microbial pathways. A snug, uniform seal prevents droplet escape, while single-use assemblies remove the need for reprocessing and the attendant risk of incomplete sterilization.
Single-Use Seal Assemblies: Eliminating Reprocessing Risks
Switching from reusable cushions to disposable, integrated seal assemblies offers multiple infection-control benefits:
Guaranteed Sterility
Each seal assembly is manufactured, packaged, and sterilized under controlled conditions. Until the point of use, the seal remains in a sterile barrier pouch, eliminating any ambiguity about its cleanliness.Zero Residual Bioburden
Disposable seals arrive free of biofilm, residual detergents, and rinse water. Reusable cushions, even when cleaned meticulously, may retain microscopic contaminants or cleaning agent residues that can irritate patient skin.Traceable Batch Coding
Single-use assemblies carry lot numbers and expiration dates, facilitating recall management and compliance audits. Infection-control teams can quickly identify and quarantine any suspect batches.No Turnaround Delay
Reprocessing reusable cushions requires time, specialized equipment, and personnel. Disposable seals are ready to use instantly—critical during emergent cases or high-turnover schedules.Cost-Effectiveness in HAI Reduction
While disposable seals carry a per-unit cost, studies have shown that reducing HAIs—even marginally—yields significant savings in patient care and liability. The elimination of reprocessing labor and disinfection materials further offsets the cost of disposables.
By adopting single-use seal assemblies, facilities eliminate the weakest link in mask hygiene, ensuring every patient receives a freshly sterilized interface and protecting staff from cross-contamination.
ZhenFu's Barrier Film and Sterile Packaging
ZhenFu Group's anesthesia masks with disposable seals employ a multi-layer barrier film system designed to maintain sterility from factory to OR:
Inner Peel-Open Pouch
A medical-grade Tyvek inner liner provides a moisture- and microbial-impermeable layer directly surrounding the seal assembly. Clinicians can open this pouch aseptically, exposing a pristine seal without direct contact.Outer Laminated Film
The outer packaging combines medical-grade polyethylene and a tear-resistant foil layer, protecting against punctures, tears, and environmental hazards during transport or storage.Laser-Printed Lot and Expiry Data
Packaging features clear, indelible text indicating lot numbers, manufacturing dates, and expiration — ensuring traceability and compliance with infection-control recordkeeping.Easy-Peel, No-Touch Opening
ZhenFu’s dual-tab design allows the seal assembly to be removed without touching its outer surfaces. Staff can don sterile gloves, peel back the tabs, and slide the assembly onto the mask body—minimizing surface contact and preserving sterility.Tamper-Evident Seals
A color-changing ink indicator in the inner pouch alerts staff if the package has been compromised by moisture or heat, adding a layer of assurance against packaging failure.
Through rigorous design and quality control, ZhenFu’s barrier film packaging transforms seal assemblies into reliably sterile, single-use components that integrate seamlessly into high-volume OR workflows.
Disposable Seal vs. Reusable Cushion Trade-Offs
When weighing the benefits of disposable seals against the traditional reusable cushions, infection-control teams must consider several factors:
Aspect
Disposable Seal
Reusable Cushion
Sterility Assurance
Guaranteed, single-use, no reprocess
Dependent on cleaning protocol quality
Biofilm Risk
Zero, fresh every time
High, if any biofilm persists
Cost per Case
Moderate (per-unit cost)
Low, amortized over many cases
Labor & Equipment
None for reprocessing
High—requires autoclave or washer-disinfector
Turnaround Time
Immediate
Variable (hours)
Environmental Impact
Increased waste volume
Less waste, but chemical effluent from disinfectants
Traceability
Full batch/lots for each seal
Limited, unless individually tracked
While disposables generate more medical waste, the trade-off of eliminating HAI risk often justifies their use, especially in vulnerable patient populations or high-risk procedures. Hybrid strategies—such as reusable mask bodies with disposable seals—strike a balance, reusing durable components while ensuring that the critical patient-contact interface is always sterile.
Workflow Integration: Reducing Touches During Donning/Doffing
Optimized workflows further amplify the infection-control benefits of advanced seal assemblies:
Pre-Set Mask Stations
In busy ORs, anesthesia carts can be pre-loaded with masks already outfitted with disposable seals. When a case begins, the clinician simply opens the inner pouch and secures the mask—no on-the-fly assembly required.Skill-Drills and Simulation
Regular staff training, using simulated mask donning scenarios, reduces hesitation and fumbled touches. Drills emphasize “no-touch” techniques for opening pouches and pulling seals into place.One-Step Strap Systems
ZhenFu’s masks incorporate single-piece straps that snap onto the mask body; they never separate from the mask, so staff handle only the outer strap when securing the device.Color-Coded Aseptic Zones
Clear visual cues—such as green tabs for sterile surfaces and red tabs for non-sterile zones—guide staff hands away from critical contact areas, minimizing inadvertent contamination.Post-Use Disposal Protocols
Immediately after extubation or mask removal, seals and masks are dropped into designated sharps/contaminated waste bins. No interim storage or reprocessing carts are needed.
By redesigning workflows around disposable, integrated seals, OR teams can reduce touches, speed up room turnover, and sustain high levels of asepsis throughout the perioperative period.

Conclusion: Seals That Protect Patients and Staff
Anesthesia masks occupy a pivotal role at the intersection of respiratory support and infection control. Advanced seal technologies—particularly single-use, disposable assemblies—deliver a double-barreled benefit: airtight containment of anesthetic gases to safeguard healthcare workers, and unwavering sterility to protect patients from HAIs.
ZhenFu Group's commitment to precision engineering, barrier-film packaging, and workflow-friendly designs ensures that every mask seal serves as a robust contamination barrier. From streamlined headgear systems that minimize handling to tamper-evident, lot-traceable packaging, these innovations transform mask seals into active defenders of OR asepsis.
In an era where both patient safety and occupational health are paramount, the right seal technology is non-negotiable. By integrating disposable seal assemblies and optimized workflows, perioperative managers can elevate their infection-control protocols, protect staff from chronic anesthetic exposure, and deliver anesthesia care with confidence—secure in the knowledge that every seal is engineered to prevent leaks, eliminate pathogens, and uphold the highest standards of clinical hygiene.
Related Products
Related News
content is empty!
CONTACT US
NO.176, Gaoxin 5th Road, High-tech Industrial Park, Rizhao City276800, Shandong Province, China +86-13396234532 +86-13396234532Copyright © 2023 ZhenFu Group All Rights Reserved. Technology By leadong.com | Sitemap | Privacy Policy















